Leaving Pumps in the Past: Little Tech with Big News for Treating Diabetes! was reported by Alex Parrott for TheSugarScience.org, 30 April 2021.
Insulin pumps have been and still are one of most convenient ways for diabetics to keep their blood sugar levels in check, but new studies in bioengineering are leading to smaller, less invasive, and more effective ways to treat diabetes.
Recent developments by Dr. Garcia-Tirado and others have led to breakthroughs for insulin pumps, but there are still issues that constant injections cause for diabetics that are unavoidable. Whether the injection is from a pump insertion, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) insertion, or insulin shot injection, they all lead to scar tissue formation. Since insulin injections are limited in location, over time injection sites are faced with the issue of scar tissue formation. This formation is inevitable and can lead to a decrease in insulin absorption or, for CGM, inaccurate readings. There are also issues with lapses in time with measurements to response or response to absorption. So how can these issues be fixed? The answer is nano tech!
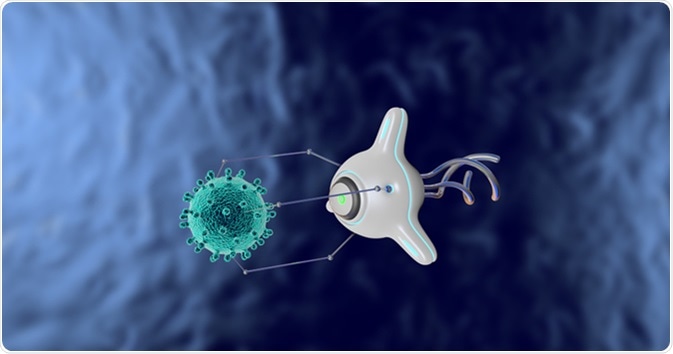 The review by Wang, Li, Hu sheds light on the micro/nano world for diabetes treatment. The first method they discuss involves using implantable nanorobotics that can form a closed-loop monitoring and delivery system. Typically made up of a hydrogel or similar biocompatible material, these nanorobotics allow for localized monitoring and delivery of a drug. In application to diabetes, this means that a measurement for blood glucose can be recorded locally at a specified in vivo location by one robot and then transmitted to another nanorobot that can then locally deliver the right amount of insulin to correctly adjust for a change in blood sugar. This technology is growing fast!
The review by Wang, Li, Hu sheds light on the micro/nano world for diabetes treatment. The first method they discuss involves using implantable nanorobotics that can form a closed-loop monitoring and delivery system. Typically made up of a hydrogel or similar biocompatible material, these nanorobotics allow for localized monitoring and delivery of a drug. In application to diabetes, this means that a measurement for blood glucose can be recorded locally at a specified in vivo location by one robot and then transmitted to another nanorobot that can then locally deliver the right amount of insulin to correctly adjust for a change in blood sugar. This technology is growing fast!
Another method discussed was microneedles and transdermal microneedle patches which would address the issue of scar tissue formation. Since these needles are smaller and not as penetrative as traditional insertions they are less likely to cause scar tissue, and if they did it would be minimal compared to current methods. An article by Yu et al, discusses a transdermal microneedle patch that is loaded with insulin and glucose responsive matrixes. When the matrixes are properly stimulated, they expand releasing insulin rapidly and efficiently. Similarly, the next article by Wu et al discusses a transdermal drug delivery system that is powered by a triboelectric nanogenerator. This method has advantages for being noninvasive and self-powered since the triboelectric generator collects energy from movements!
Read more: Little Tech with Big News for Treating Diabetes!
What You Should Know About Walmart’s Newest Low-Cost Insulin was written by Mike Hoskins for DiabetesMine.com, 30 June 2021.
 Retail giant Walmart has just added a key offering to its lineup of affordable insulins: a new ReliOn version of Novolog rapid-acting mealtime insulin that’s available at a fraction of the cost of the original name brand. On June 29, Walmart announced it would be adding this rapid-acting insulin to the much older human insulins that it’s sold under the ReliOn brand for more than two decades. This is the first time Walmart’s offered a newer analog version of insulin — modified for quicker and more effective action — in its low-cost medication lineup.
Retail giant Walmart has just added a key offering to its lineup of affordable insulins: a new ReliOn version of Novolog rapid-acting mealtime insulin that’s available at a fraction of the cost of the original name brand. On June 29, Walmart announced it would be adding this rapid-acting insulin to the much older human insulins that it’s sold under the ReliOn brand for more than two decades. This is the first time Walmart’s offered a newer analog version of insulin — modified for quicker and more effective action — in its low-cost medication lineup.
Significantly, this version of Novolog insulin will cost between 58 and 75 percent less than the current cash list price at most retail pharmacies. This will allow many people with diabetes (PWDs) to get this life-critical medication without insurance, an important factor, given the number of uninsured and underinsured, and those struggling with high-deductible insurance plans.
“We know many people with diabetes struggle to manage the financial burden of this condition, and we are focused on helping by providing affordable solutions. We also know this is a condition that disproportionately impacts underserved populations. With ReliOn NovoLog insulin, we’re adding a high-quality medication for diabetes to the already affordable ReliOn line of products and continuing our commitment to improve access and lowering cost of care,” Dr. Cheryl Pegus, executive vice president of Walmart Health & Wellness, said in a statement.
Of course, the pricing is what matters here: $72.88 per glass vial (10mL each, or 1,000 units) and $85.88 for a box of five FlexPens (each with 3mL, or 300 units). By comparison, the cash list price for name brand Novolog is $289.36 for a 10mL vial and $559 for a box of five insulin pens.
Is this the same as Novolog? Yes, it is. Walmart set the pricing, as the ReliOn program is managed by the retailer and not the pharmaceutical manufacturer.
Read more: Walmart’s Newest Low-Cost Insulin
Oil and water: long lasting insulin infusion sets and more was written by Rachel Gurlin for TheSugarScience.org, 18 Junly 2020.
How do oil and water mix? Well, they don’t. But this property of insolubility can be harnessed to fabricate some really unique structures named bijels (bicontinuous interfacially jammed emulsion gels). These bijel structures can be used as templates for biomaterials enhancing tissue integration and vascularization, potentially allowing for longer-wear insulin infusion sets.
 When creating a material suitable for implantation into the body, not only do the chemical characteristics of the material need to be considered, but the physical properties also need to be understood. The reaction to foreign materials is known as the foreign body response (FBR). Ways to mitigate the FBR include creating carefully designed porous materials, many of which have pore networks with high degrees of connectivity. However, narrow connections between these pores with sharp edges may disrupt cell migration; thus, introducing bijels, which are smooth-sailing with pores that are similarly sized and smooth all the way throughout the material. Researchers at UC Irvine create bijels, which, when heated just right, arrest (or jam) and the particles line the oil-water interfaces. These water-oil templates are then used to make solid bijel materials, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG).
When creating a material suitable for implantation into the body, not only do the chemical characteristics of the material need to be considered, but the physical properties also need to be understood. The reaction to foreign materials is known as the foreign body response (FBR). Ways to mitigate the FBR include creating carefully designed porous materials, many of which have pore networks with high degrees of connectivity. However, narrow connections between these pores with sharp edges may disrupt cell migration; thus, introducing bijels, which are smooth-sailing with pores that are similarly sized and smooth all the way throughout the material. Researchers at UC Irvine create bijels, which, when heated just right, arrest (or jam) and the particles line the oil-water interfaces. These water-oil templates are then used to make solid bijel materials, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG).
UCI researchers are hoping to use this material to coat insulin infusion sets, allowing them to remain longer in the body due to reduced FBR and enabling faster insulin delivery due to the enhanced vascularization of the material. But that’s not all; bijel templated materials have also shown favorable conditions for cell delivery applications, making it a potential method for transplanting islets into the body.
Read more: Oil and water: long lasting insulin infusion sets and more
ISLET CELL TRANSPLANT NEWS:
ViaCyte Reports Compelling Preliminary Clinical Data from Islet Cell Replacement Therapy for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes as reported on the ViaCyte.com website, 25 June 2021.
-
-
- PEC-Direct (VC-02) demonstrates first instance showing glucose-responsive insulin production, C-peptide of 0.8 ng/mL, from implanted pancreatic progenitor cells in humans
- Therapeutic effect showing increase to 88% time in range with corresponding reduction of HbA1C from 7.4% to 6.6%
- Late-breaking results presented at the American Diabetes Association’s 81st Scientific Sessions
-
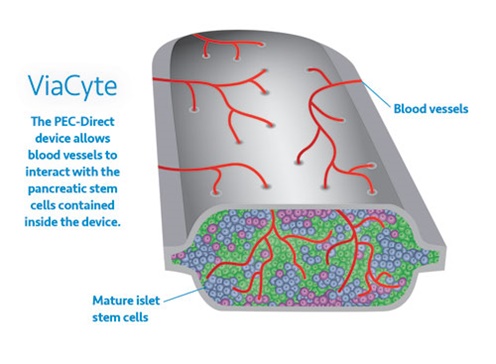 ViaCyte, Inc., a clinical-stage regenerative medicine company focused on developing cell therapies that provide a functional cure for patients with insulin-requiring diabetes, announced today compelling preliminary clinical data from its stem cell-derived islet cell replacement therapy for patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). The results reported in a late-breaking ePoster at the American Diabetes Association’s Virtual 81st Scientific Sessions showed PEC‑Direct (VC-02) demonstrates effective engraftment and production of C-peptide, a biomarker used to assess production of insulin by functional pancreatic beta cells. These data represent the first exhibition of implanted pancreatic progenitor cells producing endogenous insulin in a patient as seen by clinically relevant increases in glucose-responsive C-peptide levels, increased time in range, and reduction of HbA1C.
ViaCyte, Inc., a clinical-stage regenerative medicine company focused on developing cell therapies that provide a functional cure for patients with insulin-requiring diabetes, announced today compelling preliminary clinical data from its stem cell-derived islet cell replacement therapy for patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). The results reported in a late-breaking ePoster at the American Diabetes Association’s Virtual 81st Scientific Sessions showed PEC‑Direct (VC-02) demonstrates effective engraftment and production of C-peptide, a biomarker used to assess production of insulin by functional pancreatic beta cells. These data represent the first exhibition of implanted pancreatic progenitor cells producing endogenous insulin in a patient as seen by clinically relevant increases in glucose-responsive C-peptide levels, increased time in range, and reduction of HbA1C.
Read more: ViaCyte Reports Data from Islet Cell Replacement Therapy for T1Ds
**************************************************************************************************************
Sernova’s Principal Investigator Presents Positive New Data from Ongoing Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Clinical Trial at ATC 2021 Virtual Connect Conference was published by TheNewswire.com, 7 June 2021. Multiple patients with sustained clinical benefit, including positive fasting serum C-peptide (a biomarker of insulin produced by Sernova’s Cell Pouch islets) detected in their bloodstream
 Sernova Corp. (TSXV:SVA) (OTC:SEOVF) (FSE/XETRA:PSH), a leading clinical-stage regenerative medicine therapeutics company today announced that its principal investigator, Dr. Piotr Witkowski, presented new preliminary data from Sernova’s ongoing U.S. Phase I/II T1D clinical trial at the University of Chicago. Dr. Witkowski’s presented the data at the American Transplant Congress (ATC) 2021 Virtual Connect conference on Saturday June 5, 2021.
Sernova Corp. (TSXV:SVA) (OTC:SEOVF) (FSE/XETRA:PSH), a leading clinical-stage regenerative medicine therapeutics company today announced that its principal investigator, Dr. Piotr Witkowski, presented new preliminary data from Sernova’s ongoing U.S. Phase I/II T1D clinical trial at the University of Chicago. Dr. Witkowski’s presented the data at the American Transplant Congress (ATC) 2021 Virtual Connect conference on Saturday June 5, 2021.
Dr. Witkowski’s presentation entitled “Islet Allotransplantation Into The Pre-Vascularized Sernova Cell PouchTM Device – Preliminary Results Of The Phase I/II Prospective, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study At University of Chicago” highlighted the following key points:
-
-
- 6 patients are implanted with Cell Pouches and continue to meet the study’s primary safety endpoint;
- 5 patients have now been transplanted with at least one dose of therapeutic cells (insulin producing islets) and are in different stages of the clinical trial; and
- most significantly, positive fasting serum C-peptide has been detected in the bloodstream of 4 patients so far. C-peptide is a biomarker for insulin produced by the islets in the Cell Pouch.
-
In addition to the continued confirmation of ongoing safety and tolerability in all currently enrolled patients, Dr. Witkowski provided further updates on the longest treated study patients. These patients continue to show defined clinical benefit associated with ongoing efficacy indicators including:
-
-
- reduction/elimination in the need for daily injectable insulin
- continued improvement, i.e. reduction/elimination, in Severe Hypoglycemic Events (SHE);
- persistent detection of fasting and stimulated C-peptide in patients’ bloodstream;
- reduction in HbA1c; and
- continued improvement of glucose control determined through patient blinded Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and measured by reduction of Time Above Range (TAR) and increase of Time in Range (TIR).
-
**************************************************************************************************************
Humacyte Presents on Biovascular Pancreas Transplantation for T1D Treatment was posted on Intrado GlobeNewsWire.com, 8 June 2021.
-
-
- Laboratory and preclinical models demonstrate biovascular pancreas platform technology may provide method to transplant islet cells that produce insulin in Type 1 diabetes patients
- Data presented at American Transplant Congress 2021 Virtual Connect
-
 Humacyte, Inc., a clinical-stage biotechnology platform company developing universally implantable bioengineered human tissue at commercial scale, presented initial data from laboratory and preclinical models demonstrating the potential to engineer a biovascular pancreas to deliver islet cells to produce insulin in Type 1 diabetic patients. The data show that pancreatic islet cells embedded in the outer matrix of an acellular vessel can create a biovascular pancreas transplant. In preclinical models, the islets on the surface of the biovascular pancreas sensed blood glucose and delivered insulin to the animal subjects, in therapeutic quantities. In addition to glucose sensing and insulin delivery, the biovascular pancreas supported islet graft oxygenation and vascularization, reducing islet hypoxia and cell death as compared to control, non-vascular implants which displayed islet death and did not correct blood glucose levels.
Humacyte, Inc., a clinical-stage biotechnology platform company developing universally implantable bioengineered human tissue at commercial scale, presented initial data from laboratory and preclinical models demonstrating the potential to engineer a biovascular pancreas to deliver islet cells to produce insulin in Type 1 diabetic patients. The data show that pancreatic islet cells embedded in the outer matrix of an acellular vessel can create a biovascular pancreas transplant. In preclinical models, the islets on the surface of the biovascular pancreas sensed blood glucose and delivered insulin to the animal subjects, in therapeutic quantities. In addition to glucose sensing and insulin delivery, the biovascular pancreas supported islet graft oxygenation and vascularization, reducing islet hypoxia and cell death as compared to control, non-vascular implants which displayed islet death and did not correct blood glucose levels.
“These data demonstrate the potential to engineer a biovascular pancreas based on our HAV platform technology, that may effectively deliver islet cells that can produce insulin for people with Type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetics no longer make their own insulin, and currently face limited curative treatment options including pancreas transplant, which is a morbid procedure. Without transplantation, Type 1 diabetics are committed to life-long insulin use,” said Jeffrey Lawson, M.D., Ph.D., Chief Surgical Officer of Humacyte. “Our approach to leverage the HAV to deliver islet cells may overcome major challenges faced by transplantation of islets, including ensuring islets receive adequate oxygen. We’re encouraged by these data and look forward to continuing to evaluate the HAV for therapeutic cell transplantation.”
The data were presented June 6 by Dr. Lawson at the American Transplant Congress 2021 Virtual Connect and will be available on Humacyte.com.
Read more: Humacyte Presents In Vivo Data on Biovascular Pancreas Transplantation for Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
Pramlintide-insulin co-formulation improves time in range in type 1 diabetes was presented at the ADA 81st Scientific Sessions and reported on Healio.com/Endocrinology, 1 July 2021.
 ADO09, a co-formulation of pramlintide and insulin A21G, was associated with better glucose levels, improved time in range and more weight loss among people with type 1 diabetes compared with insulin aspart, according to a presenter.
ADO09, a co-formulation of pramlintide and insulin A21G, was associated with better glucose levels, improved time in range and more weight loss among people with type 1 diabetes compared with insulin aspart, according to a presenter.
“ADO09 is a new and innovative co-formulation of two hormones missing in type 1 diabetes: insulin and its little sister amylin, co-secreted with insulin by the beta cells of the pancreas,” Gregory Meiffren, PhD, director of clinical development, PKPD and biology at Adocia, told Healio. “When we compared the effect of ADO09 to that of insulin aspart, one of the gold standard prandial insulins, ADO09 improved postprandial blood glucose control, reduced insulin doses and lowered body weight in subjects with type 1 diabetes who use large insulin doses every day.”
“Our results demonstrate that the fixed combination of the two hormones blunts the postprandial blood glucose excursions, which remains the most difficult period of the day to control in type 1 diabetes,” Meiffren said. “Additionally, achieving blood glucose targets generally requires intensive insulin therapy, which, however, results in body weight gain. Knowing the obesity epidemic now also hits type 1 diabetes subjects, it is an interesting perspective to develop a postprandial co-formulation which reduces body weight.”
Read more: Pramlintide-insulin co-formulation improves time in range in T1D


wow I have been following Humacyte for many years. I am impressed. Maybe a stock market darling in the offing?
The Walmart insulin sounds like the generic from Lilly. Well when some people do a great job they get canceled. Just saying.
rick